✔️ 문제 설명 (펼치기)
문제
동물원에서 막 탈출한 원숭이 한 마리가 세상구경을 하고 있다. 그 녀석은 말(Horse)이 되기를 간절히 원했다. 그래서 그는 말의 움직임을 유심히 살펴보고 그대로 따라 하기로 하였다. 말은 말이다. 말은 격자판에서 체스의 나이트와 같은 이동방식을 가진다. 다음 그림에 말의 이동방법이 나타나있다. x표시한 곳으로 말이 갈 수 있다는 뜻이다. 참고로 말은 장애물을 뛰어넘을 수 있다.
| x | x | |||
| x | x | |||
| 말 | ||||
| x | x | |||
| x | x |
근데 원숭이는 한 가지 착각하고 있는 것이 있다. 말은 저렇게 움직일 수 있지만 원숭이는 능력이 부족해서 총 K번만 위와 같이 움직일 수 있고, 그 외에는 그냥 인접한 칸으로만 움직일 수 있다. 대각선 방향은 인접한 칸에 포함되지 않는다.
이제 원숭이는 머나먼 여행길을 떠난다. 격자판의 맨 왼쪽 위에서 시작해서 맨 오른쪽 아래까지 가야한다. 인접한 네 방향으로 한 번 움직이는 것, 말의 움직임으로 한 번 움직이는 것, 모두 한 번의 동작으로 친다. 격자판이 주어졌을 때, 원숭이가 최소한의 동작으로 시작지점에서 도착지점까지 갈 수 있는 방법을 알아내는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
입력
첫째 줄에 정수 K가 주어진다. 둘째 줄에 격자판의 가로길이 W, 세로길이 H가 주어진다. 그 다음 H줄에 걸쳐 W개의 숫자가 주어지는데, 0은 아무것도 없는 평지, 1은 장애물을 뜻한다. 장애물이 있는 곳으로는 이동할 수 없다. 시작점과 도착점은 항상 평지이다. W와 H는 1이상 200이하의 자연수이고, K는 0이상 30이하의 정수이다.
출력
첫째 줄에 원숭이의 동작수의 최솟값을 출력한다. 시작점에서 도착점까지 갈 수 없는 경우엔 -1을 출력한다.
✔️ 문제 풀이
• bfs의 탐색 범위를 2가지로 설정한다.
1. 말처럼 나이트 이동방식 총 8가지 경우의 수
int[] hx = {-2, -1, 1, 2, -2, -1, 1, 2};
int[] hy = {-1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1};
2. 인접한 좌표 방문 4가지수
int[] dx = {1,-1,0, 0};
int[] dy = {0,0,-1, 1};
• Point class 설정
private int x; //x 좌표
private int y; //y 좌표
private int k_cnt; //말처럼(나이트 이동) 이동횟수
private int total; //총 이동횟수
[정답 코드]
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class Main{
static int[] hx = {-2, -1, 1, 2, -2, -1, 1, 2};
static int[] hy = {-1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1};
static int[] dx = {1,-1,0, 0};
static int[] dy = {0,0,-1, 1};
public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st ;
int k = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int w = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int h = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int[][] arr = new int [h][w];
for(int i = 0; i<h; i++){
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for(int j = 0; j<w; j++){
arr[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
int next_x, next_y;
Queue<Point> q = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[][][] visited = new boolean[h][w][k+1];
q.add(new Point(0,0,0, 0));
while(!q.isEmpty()){
Point current = q.poll();
if(current.x== w-1 && current.y ==h-1) {
System.out.println(current.total);
return;
}
if(current.k_cnt < k) {
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
next_x = current.x + hx[i];
next_y = current.y + hy[i];
if (next_x < 0 || next_x >= w || next_y < 0 || next_y >= h || arr[next_y][next_x] == 1)
continue;
if(visited[next_y][next_x][current.k_cnt+1])
continue;
q.add(new Point(next_x, next_y, current.k_cnt + 1, current.total+1));
visited[next_y][next_x][current.k_cnt+1] = true;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i<4; i++){
next_x = current.x + dx[i];
next_y = current.y + dy[i];
if(next_x<0 || next_x>=w || next_y<0 || next_y>= h|| arr[next_y][next_x] == 1)
continue;
if(visited[next_y][next_x][current.k_cnt])
continue;
q.add(new Point(next_x, next_y, current.k_cnt, current.total+1));
visited[next_y][next_x][current.k_cnt] = true;
}
}
System.out.println(-1);
}
public static class Point{
private int x;
private int y;
private int k_cnt;
private int total;
public Point(int x, int y, int k_cnt, int total){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.k_cnt = k_cnt;
this.total = total;
}
}
}
[시간 초과 풀이]
이전의 방문 여부와 관계없이 도착지에 도달할때까지 경로를 찾을 수 있도록 했다.
대신 -1를 반환해야하는 경로가 없는 경우에는 검사해야하는 경우의 수가 많으므로, 조건문을 설정해주었다.
목적지 도달까지 인접한 좌표만으로 가는 경우의 수가 원숭이의 동작수의 최댓값이 된다.
이 최댓값을 넘어가면 목적지에 도달할 수 없는 경우로 간주하고 -1을 출력하였다.
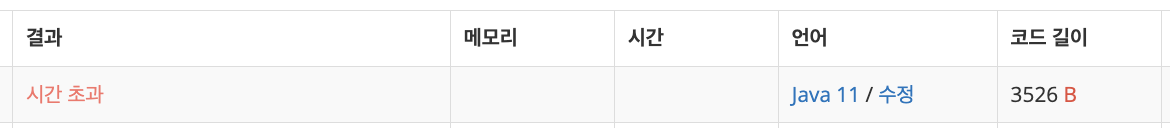
하지만, 결과는 .... 시간초과 .... !!!!!
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class Main{
static int[] hx = {-2, -1, 1, 2, -2, -1, 1, 2};
static int[] hy = {-1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1};
static int[] dx = {1,-1,0, 0};
static int[] dy = {0,0,-1, 1};
public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st ;
int k = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int w = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int h = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int[][] arr = new int [h][w];
for(int i = 0; i<h; i++){
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for(int j = 0; j<w; j++){
arr[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
int next_x, next_y;
Queue<Point> q = new LinkedList<>();
// boolean[][] visited = new boolean[h][w];
q.add(new Point(0,0,0, 0));
int cnt = 0;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
Point current = q.poll();
if(current.x== w-1 && current.y ==h-1) {
System.out.println(current.total);
return;
}
if(current.total > w+h-2){
System.out.println(-1);
return;
}
if(current.k_cnt < k) {
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
next_x = current.x + hx[i];
next_y = current.y + hy[i];
if (next_x < 0 || next_x >= w || next_y < 0 || next_y >= h || arr[next_y][next_x] == 1)
continue;
q.add(new Point(next_x, next_y, current.k_cnt + 1, current.total+1));
}
}
for(int i = 0; i<4; i++){
next_x = current.x + dx[i];
next_y = current.y + dy[i];
if(next_x<0 || next_x>=w || next_y<0 || next_y>= h|| arr[next_y][next_x] == 1)
continue;
q.add(new Point(next_x, next_y, current.k_cnt, current.total+1));
}
}
System.out.println(-1);
}
public static class Point{
private int x;
private int y;
private int k_cnt;
private int total;
public Point(int x, int y, int k_cnt, int total){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.k_cnt = k_cnt;
this.total = total;
}
}
}
시간을 줄일 수 있는 방법을 생각해보니 떠오르지 않아서 풀이를 참조하였다 !
생각해내는게 왤캐 어렵징 ㅠㅠㅠ
'Coding Test > 백준 알고리즘 풀이' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준] N과M (1), (2), (3), (4) : 자바 백트레킹 (0) | 2024.10.01 |
|---|---|
| [백준] 7576 토마토 : 자바 BFS [골드5] (0) | 2024.10.01 |
| [백준] 15486 퇴사2 (자바) : DP [골드 5] (1) | 2024.09.17 |
| [백준] 11055 가장 큰 증가하는 부분 수열 (자바) : DP [실버2] (0) | 2024.08.29 |
| [백준] 11053번 가장 긴 증가하는 부분 수열 (자바) : DP [실버 2] (6) | 2024.08.28 |


